I believe many people are not unfamiliar with PCB circuit boards, and may often hear about them in their daily lives. However, they may not be very familiar with PCBA and may even confuse it with PCB. So what is PCB? How did PCBA evolve? What is the difference between PCB and PCBA? How can solution providers efficiently find suppliers for research and development production?
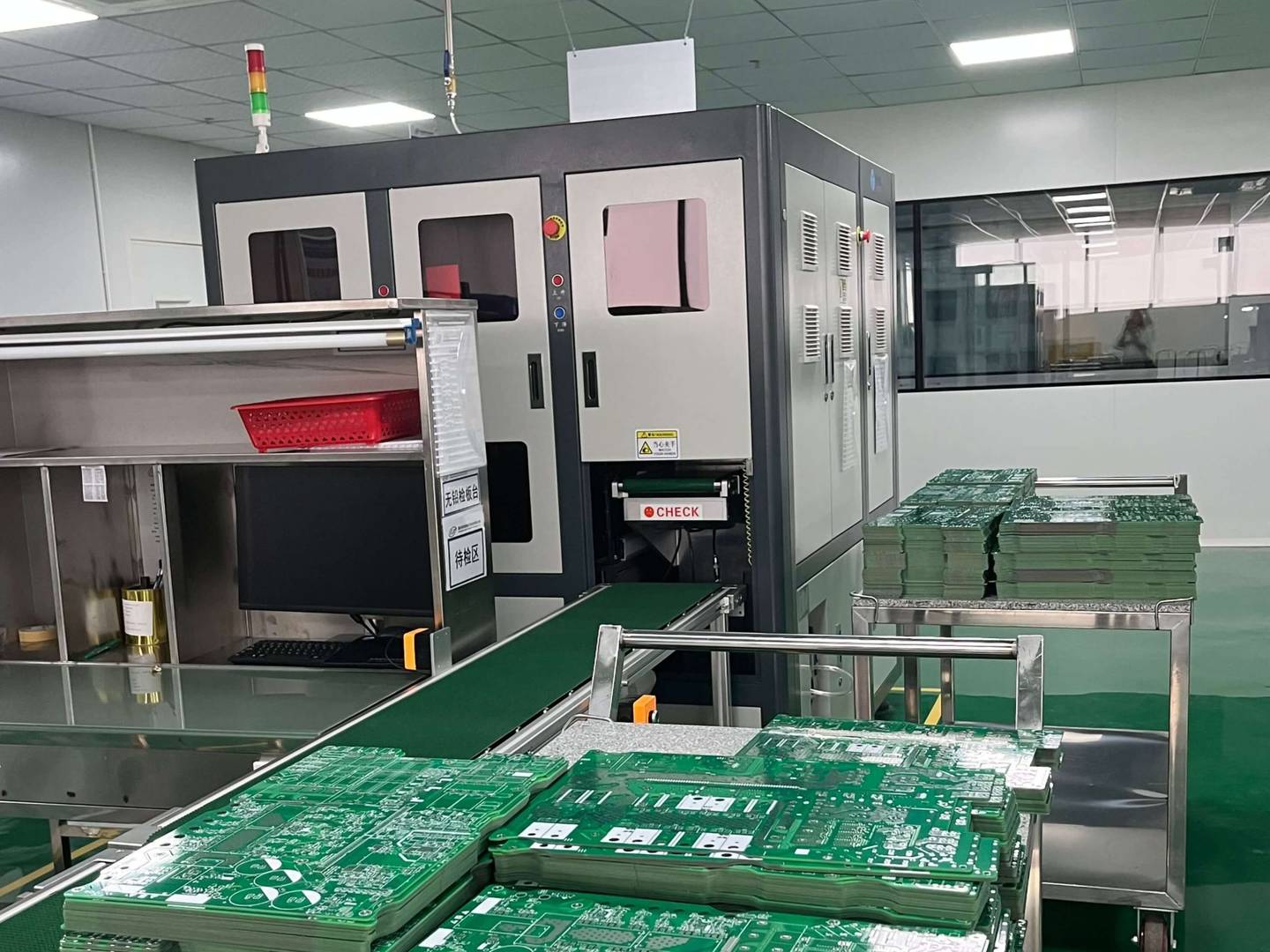
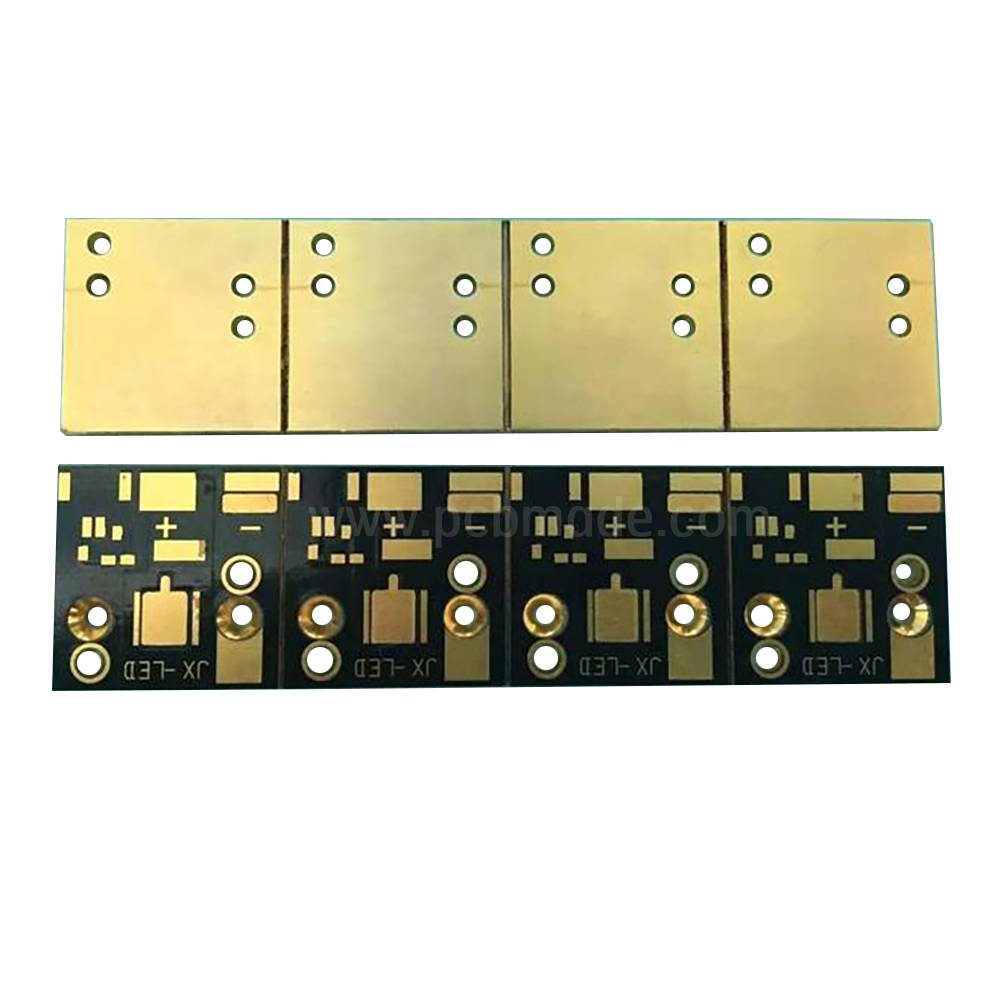
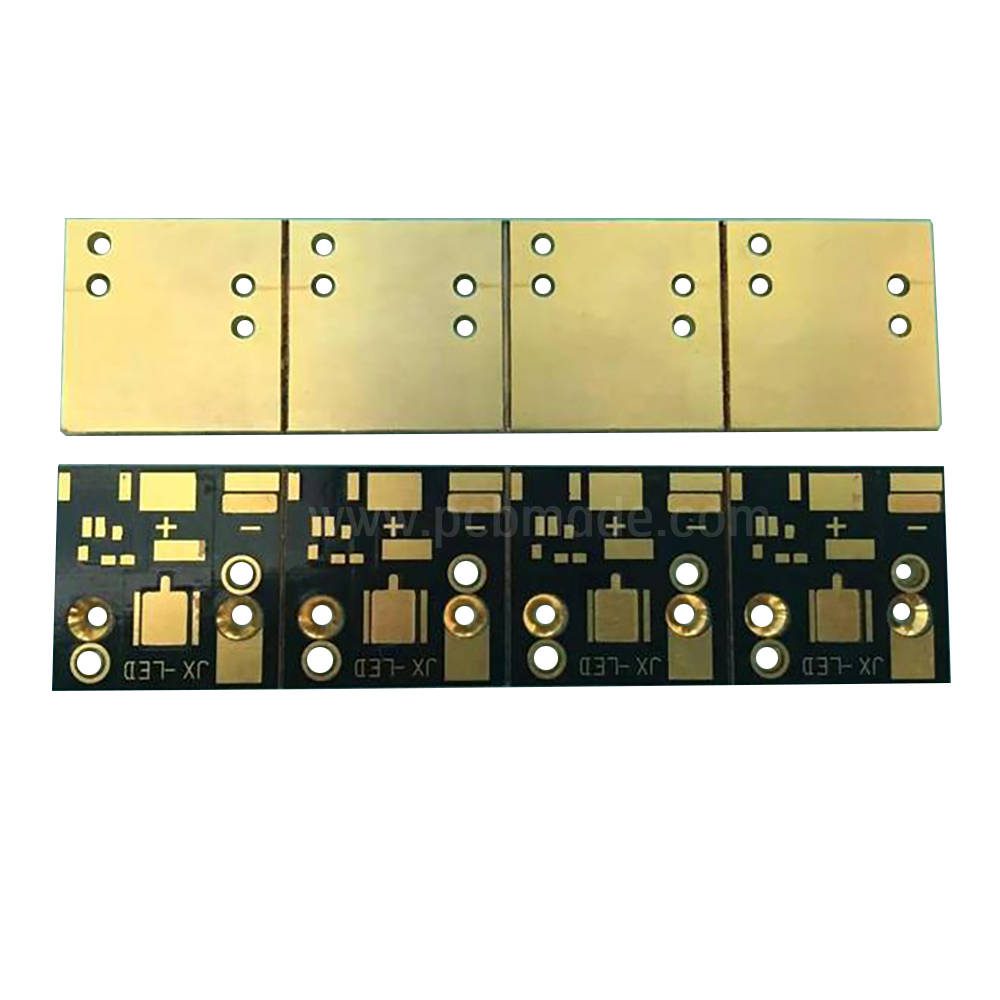
Firstly, let’s understand what PCB is. PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board, which is made using electronic printing technology and is therefore called a “printed” circuit board. The fundamental difference between PCB and PCBA is that PCB itself is an empty circuit board that does not contain any electronic components. It looks like a green board with dividing lines and holes, and such an empty circuit board cannot function properly. If PCBA is the core of electronic products, then PCB is the carrier of this core and the support of electronic components, enabling electrical connections between electronic components.
Printed circuit boards are composed of insulating substrates, connecting wires, and solder pads for electronic components. They serve as conductive lines and insulating substrates, and are widely used in the production and manufacturing of electronic products.
There are many subcategories of PCB, such as substrate characterization, board and PCB layers. Taking board as an example, it can be divided into:
1. FR-4 board
FR-4 board is one of the most commonly used PCB boards, composed of fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin. It has the following characteristics:
Mechanical strength, heat resistance, flame retardancy, electrical performance

2. High frequency board
High frequency board is a PCB board specifically designed for designing high-frequency circuits, mainly including the following types:
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), RF board, Rogers board
3. Metal substrate
A metal substrate is formed by covering a layer of metal material on an FR-4 board or high-frequency board. Common metal substrates include:
Aluminum substrate, copper substrate, ceramic substrate

4. Flexible substrate
A flexible substrate is a PCB made of flexible materials and has the following characteristics:
Flexible, lightweight and compact, high-density wiring

5. High temperature substrate
High temperature substrates have good high-temperature resistance and can maintain the reliability and stability of circuits in high-temperature environments. At the same time, high-temperature substrates also have the characteristic of chemical corrosion resistance, which is suitable for applications in some special environments.
6. Composite materials
In addition to the common PCB boards mentioned above, there are also some composite materials used in the manufacturing of PCBs. These materials are composed of stacked combinations of multiple base materials to achieve specific functional and performance requirements. For example:
① Metal/ceramic composite materials: have high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, suitable for applications in high-power and high-temperature environments.
② Polyimide (PI) composite material: Polyimide is a high-performance engineering plastic with excellent high temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties, suitable for high demand electronic devices.
7. Other materials
In addition to the main materials mentioned above, there are also other materials used in the manufacturing of PCB boards, such as phenolic resin (FR-1 and XPC), epoxy fiberglass cloth substrates (CEM-1 and CEM-3), etc.
Different materials have their own characteristics and are suitable for different application scenarios; Engineering considers different application scenarios and selects different materials while designing products
Yizhen Technology can produce PCBs according to customer needs by providing manufacturing engineering drawings, CAD, and production process flow.